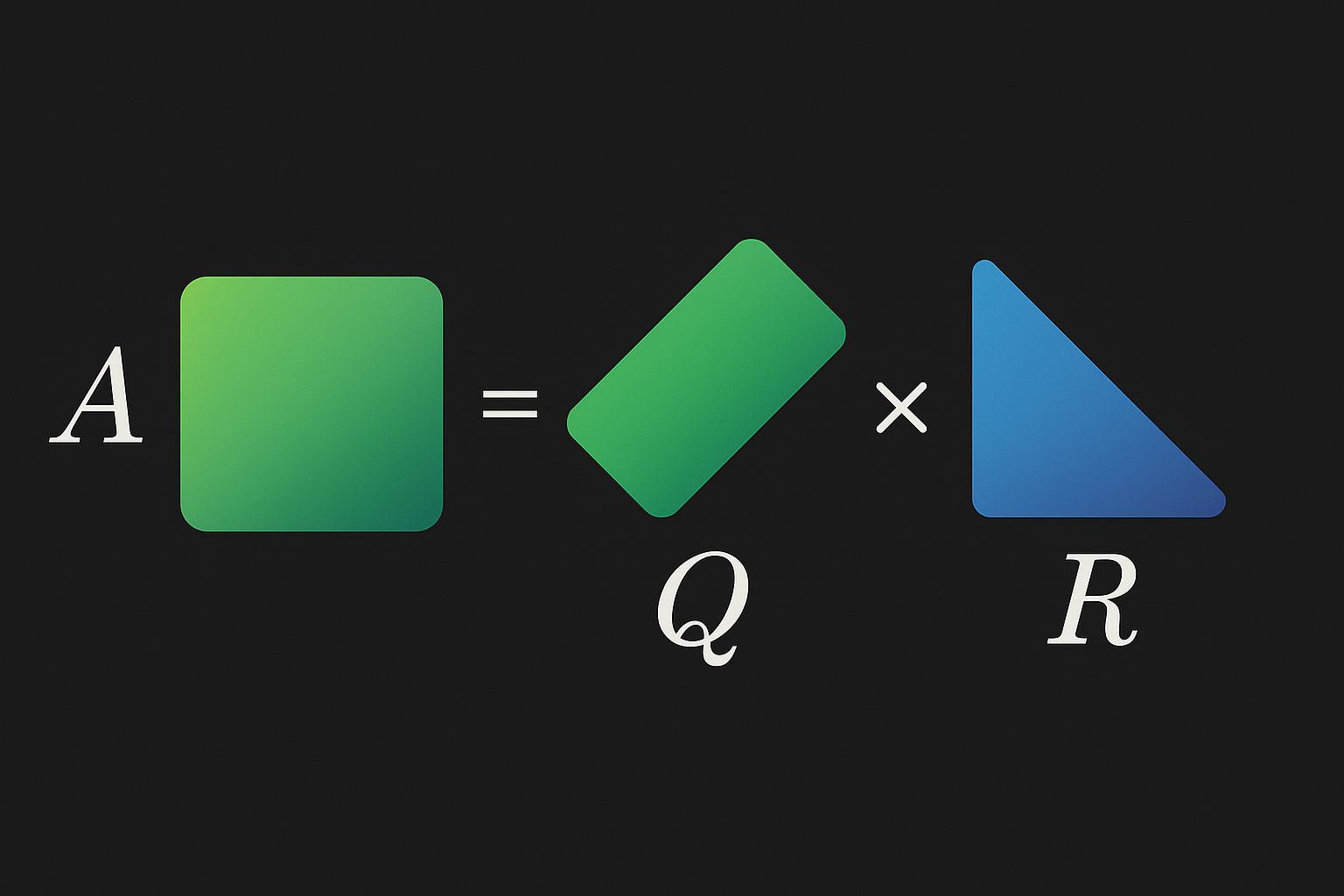
QR decomposition factors a matrix into orthogonal Q and upper triangular R. Used for solving linear systems, eigenvalue computation, and least squares.
The decomposition
For matrix A (m×n, m ≥ n):
$$A = QR$$
Where:
- Q is m×n with orthonormal columns (Q^TQ = I)
- R is n×n upper triangular
Interactive demo: QR Decomposition Animation
Why orthogonal matrices are nice
Orthogonal Q means:
- Q^T = Q^(-1) (inverse is just transpose)
- ||Qx|| = ||x|| (preserves norms)
- Numerically stable
Gram-Schmidt process
Classic algorithm to construct Q and R.
Orthogonalize columns of A one by one:
def gram_schmidt(A):
m, n = A.shape
Q = np.zeros((m, n))
R = np.zeros((n, n))
for j in range(n):
v = A[:, j].copy()
# Subtract projections onto previous q's
for i in range(j):
R[i, j] = Q[:, i] @ A[:, j]
v -= R[i, j] * Q[:, i]
R[j, j] = np.linalg.norm(v)
Q[:, j] = v / R[j, j]
return Q, R
Problem: numerically unstable. Don’t use in practice.
In practice
Just use the library:
import numpy as np
A = np.random.randn(5, 3)
Q, R = np.linalg.qr(A)
# Verify
np.allclose(A, Q @ R) # True
np.allclose(Q.T @ Q, np.eye(3)) # True (orthonormal)
Solving linear systems
Ax = b with QR decomposition:
$$Ax = b$$ $$QRx = b$$ $$Rx = Q^Tb$$
R is triangular → solve by back substitution. Faster and more stable than direct inverse.
Q, R = np.linalg.qr(A)
x = np.linalg.solve(R, Q.T @ b)
Least squares
When Ax = b has no solution (overdetermined), find x minimizing ||Ax - b||².
QR gives the answer: $$\hat{x} = R^{-1}Q^Tb$$
# Least squares via QR
def least_squares_qr(A, b):
Q, R = np.linalg.qr(A)
return np.linalg.solve(R, Q.T @ b)
# Same as
x = np.linalg.lstsq(A, b, rcond=None)[0]
More stable than normal equations (A^TAx = A^Tb).
QR algorithm for eigenvalues
Iteratively apply QR decomposition to find eigenvalues:
def qr_algorithm(A, num_iters=100):
for _ in range(num_iters):
Q, R = np.linalg.qr(A)
A = R @ Q
return np.diag(A) # eigenvalues on diagonal
Converges to diagonal matrix (for real eigenvalues). With shifts and deflation, this is how eigenvalues are actually computed.
Full vs reduced QR
Full QR: Q is m×m, R is m×n Reduced QR: Q is m×n, R is n×n
numpy.linalg.qr returns reduced by default.
QR decomposition visualized! If this helped, star ML Animations and share with your math-loving friends!