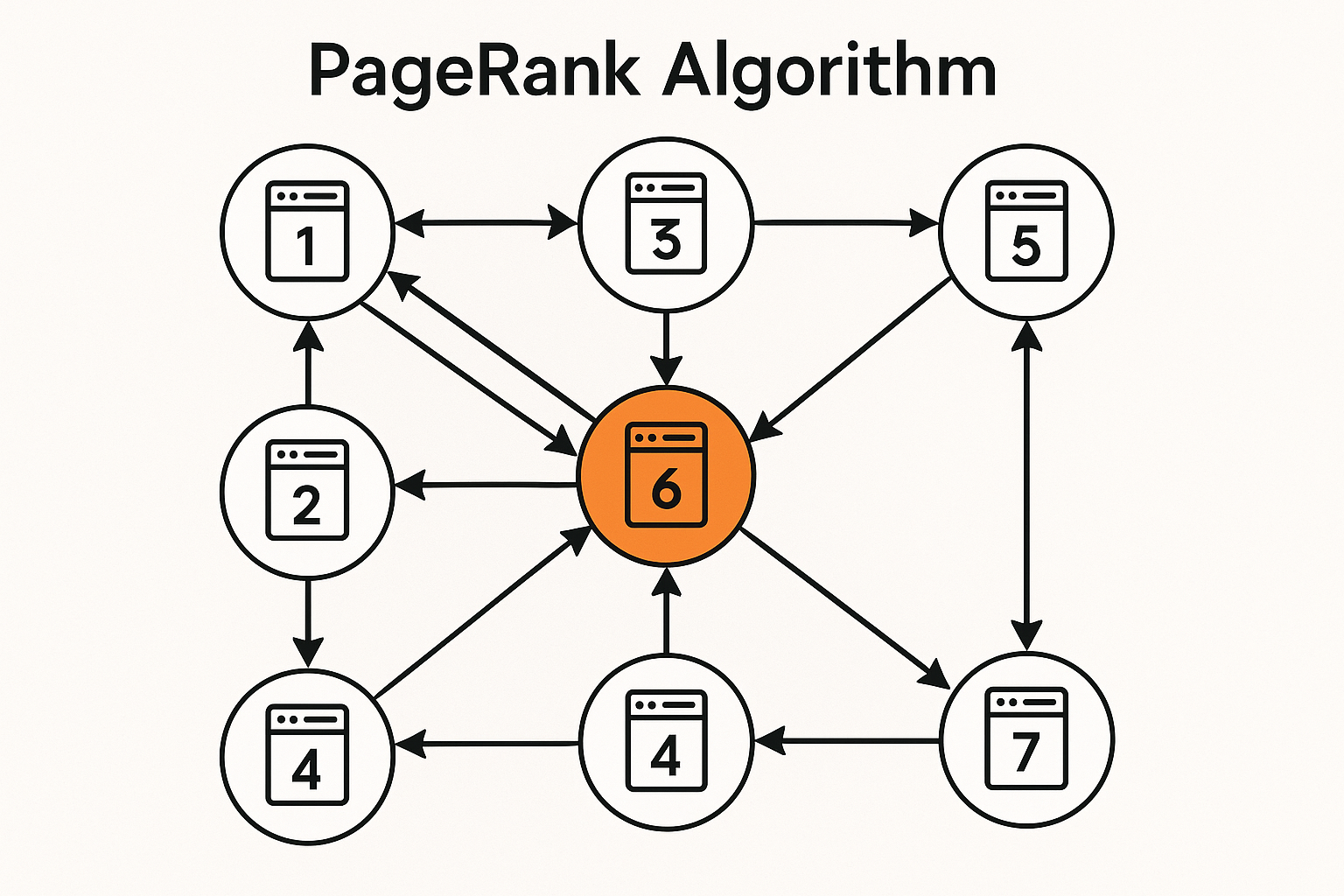
Not all links are equal. A link from Wikipedia matters more than a random blog. But how does Wikipedia become important? Because important pages link to it. This circular definition is exactly what PageRank captures.
The intuition
Imagine a random web surfer:
- At each page, randomly click a link
- Occasionally (probability d), jump to random page instead
PageRank = probability of finding the surfer at each page in the long run.
Important pages are visited more often.
Interactive demo: PageRank Animation
The formula
$$PR(p) = \frac{1-d}{N} + d \sum_{q \in B_p} \frac{PR(q)}{L(q)}$$
Where:
- d: damping factor (typically 0.85)
- N: total number of pages
- B_p: pages linking to p
- L(q): number of outgoing links from q
Matrix formulation
Let M be transition matrix: M[i,j] = 1/L(j) if j links to i, else 0.
$$\mathbf{r} = d \cdot M \cdot \mathbf{r} + \frac{1-d}{N} \mathbf{1}$$
PageRank r is the eigenvector (stationary distribution).
Power iteration
Simple algorithm to compute:
def pagerank(adjacency_list, d=0.85, max_iter=100, tol=1e-6):
N = len(adjacency_list)
r = {node: 1/N for node in adjacency_list}
for _ in range(max_iter):
r_new = {}
for node in adjacency_list:
incoming = [n for n, links in adjacency_list.items() if node in links]
rank_sum = sum(r[n] / len(adjacency_list[n]) for n in incoming
if adjacency_list[n])
r_new[node] = (1-d)/N + d * rank_sum
# Check convergence
diff = sum(abs(r_new[n] - r[n]) for n in r)
r = r_new
if diff < tol:
break
return r
Example
A → B, C
B → C
C → A
Initial: all 1/3
After iterations:
- A: 0.387 (C links to it)
- B: 0.214 (only A links to it)
- C: 0.399 (both A and B link to it)
C most important - receives links from both others.
Handling edge cases
Dangling nodes: Pages with no outgoing links. Distribute their rank equally to all pages.
Spider traps: Group of pages only linking to each other. Damping factor prevents getting stuck.
Beyond web search
PageRank concepts apply to:
- Citation networks (important papers)
- Social networks (influential users)
- Recommendation systems
- Any graph where importance flows through edges
Connection to eigenvectors
PageRank is the dominant eigenvector of the Google matrix:
$$G = d \cdot M + \frac{1-d}{N} \mathbf{1}\mathbf{1}^T$$
This is why power iteration converges - it finds the largest eigenvector.
PageRank algorithm explained! Support ML Animations with a ⭐ and share this classic algorithm breakdown!