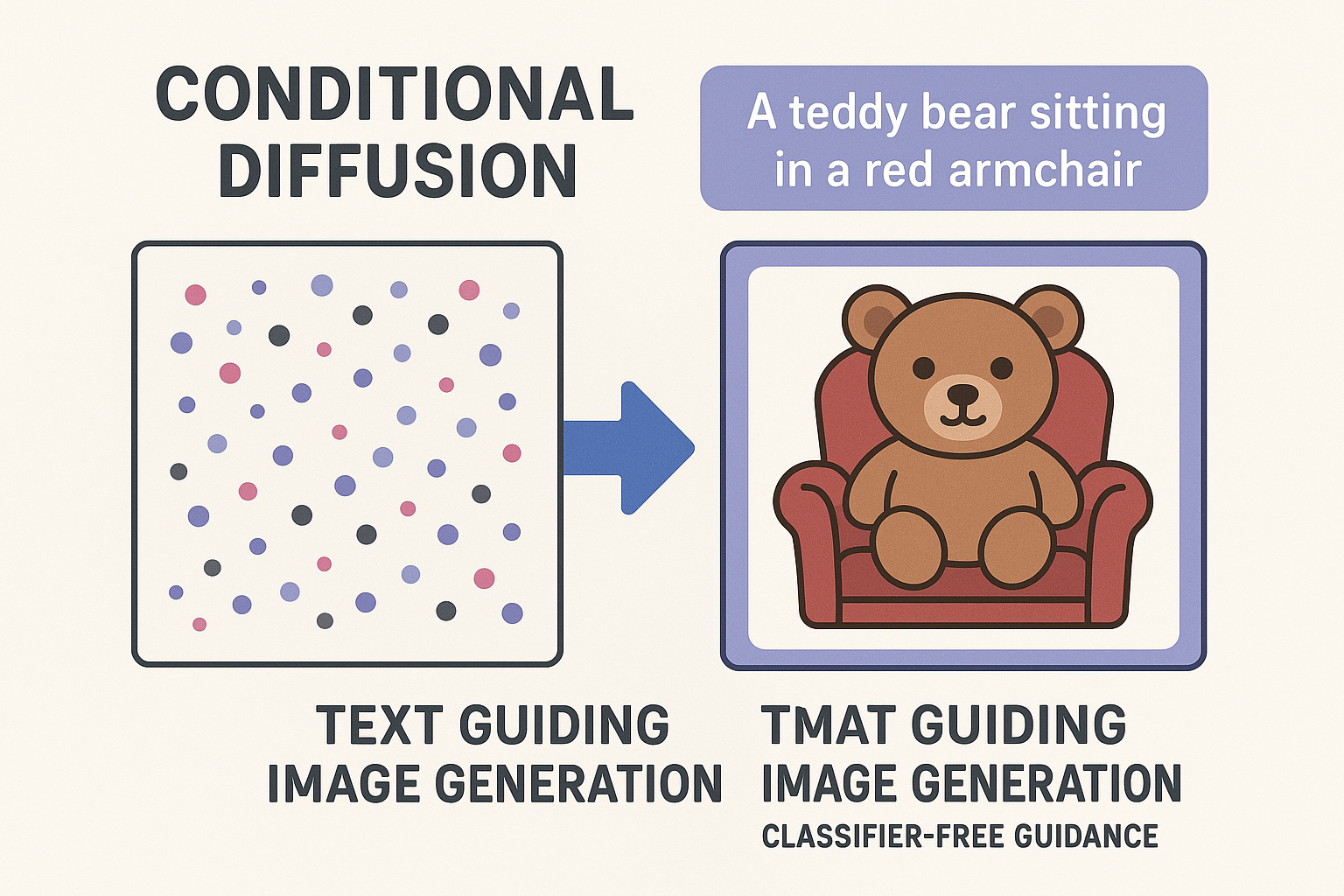
Unconditional diffusion generates random images. Conditioning lets you control what’s generated. Text conditioning enables: “a cat wearing a hat” → image of cat with hat.
Part 7 of 7 in the Diffusion Models series.
Types of conditioning
- Class: Generate specific category (dog, cat, car)
- Text: Natural language description
- Image: Edit or transform existing image
- Layout: Bounding boxes, segmentation maps
Interactive demo: CLIP Encoder Animation
Class conditioning
Simplest form. Embed class label, add to timestep embedding:
class ClassConditionedUNet(UNet):
def __init__(self, num_classes):
super().__init__()
self.class_emb = nn.Embedding(num_classes, 256)
def forward(self, x, t, class_label):
t_emb = self.time_emb(t)
c_emb = self.class_emb(class_label)
combined_emb = t_emb + c_emb # Simple addition
# Rest of forward pass uses combined_emb
...
Text conditioning
Text → embedding → guide denoising
Text encoder: CLIP or T5
from transformers import CLIPTextModel, CLIPTokenizer
tokenizer = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-large-patch14")
text_encoder = CLIPTextModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-large-patch14")
def encode_text(prompt):
tokens = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt", padding=True, truncation=True)
text_emb = text_encoder(**tokens).last_hidden_state
return text_emb # (batch, seq_len, 768)
Cross-attention for text
U-Net attends to text embeddings:
class CrossAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, query_dim, context_dim):
super().__init__()
self.to_q = nn.Linear(query_dim, query_dim)
self.to_k = nn.Linear(context_dim, query_dim)
self.to_v = nn.Linear(context_dim, query_dim)
self.to_out = nn.Linear(query_dim, query_dim)
def forward(self, x, context):
# x: image features (batch, h*w, dim)
# context: text embeddings (batch, seq_len, context_dim)
q = self.to_q(x)
k = self.to_k(context)
v = self.to_v(context)
attn = torch.softmax(q @ k.transpose(-2, -1) / math.sqrt(q.shape[-1]), dim=-1)
out = attn @ v
return self.to_out(out)
Image features query text embeddings. Relevant text influences each spatial location.
Modified residual block
class ResBlockWithCrossAttn(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, context_dim):
super().__init__()
self.res_block = ResBlock(channels, channels, time_emb_dim=256)
self.cross_attn = CrossAttention(channels, context_dim)
self.norm = nn.GroupNorm(8, channels)
def forward(self, x, t_emb, context):
# Self-attention / conv processing
x = self.res_block(x, t_emb)
# Reshape for attention
b, c, h, w = x.shape
x_flat = x.view(b, c, h*w).transpose(1, 2)
# Cross-attention with text
x_flat = x_flat + self.cross_attn(self.norm(x_flat), context)
# Reshape back
x = x_flat.transpose(1, 2).view(b, c, h, w)
return x
Classifier-free guidance
During training, randomly drop condition (replace with null):
def train_step(model, x_0, condition):
# Randomly drop condition 10% of time
if random.random() < 0.1:
condition = None
# Normal training
...
During sampling, amplify difference:
def guided_sample(model, x, t, condition, guidance_scale=7.5):
# Unconditional
noise_uncond = model(x, t, condition=None)
# Conditional
noise_cond = model(x, t, condition=condition)
# Guide toward condition
noise = noise_uncond + guidance_scale * (noise_cond - noise_uncond)
return noise
Higher guidance = follows prompt more closely (but less diversity).
Stable Diffusion architecture
Text → CLIP → text embeddings
↓
┌─────────────────┐
Noise → │ U-Net │ → predicted noise
│ (with cross- │
│ attention) │
└─────────────────┘
↑
timestep embedding
Plus: works in latent space (VAE encodes/decodes images).
Putting it all together
@torch.no_grad()
def generate(prompt, steps=50, guidance_scale=7.5):
# Encode text
text_emb = encode_text(prompt)
null_emb = encode_text("")
# Start from noise
x = torch.randn(1, 4, 64, 64, device=device) # latent space
for t in ddim_timesteps(steps):
# Unconditional and conditional predictions
noise_uncond = model(x, t, null_emb)
noise_cond = model(x, t, text_emb)
# Guided noise
noise = noise_uncond + guidance_scale * (noise_cond - noise_uncond)
# DDIM step
x = ddim_step(x, noise, t)
# Decode latent to image
image = vae.decode(x)
return image
# Generate!
image = generate("a serene lake at sunset with mountains")
The series complete
- Tensors: the data format
- Neural networks: the building blocks
- Noise: the forward/reverse process
- U-Net: the architecture
- Training: learning to denoise
- Sampling: generating images
- Conditioning: controlling generation
You now understand diffusion end-to-end!
Diffusion series complete! 🎉 If this helped you understand text-to-image, star ML Animations and share the whole series with others!