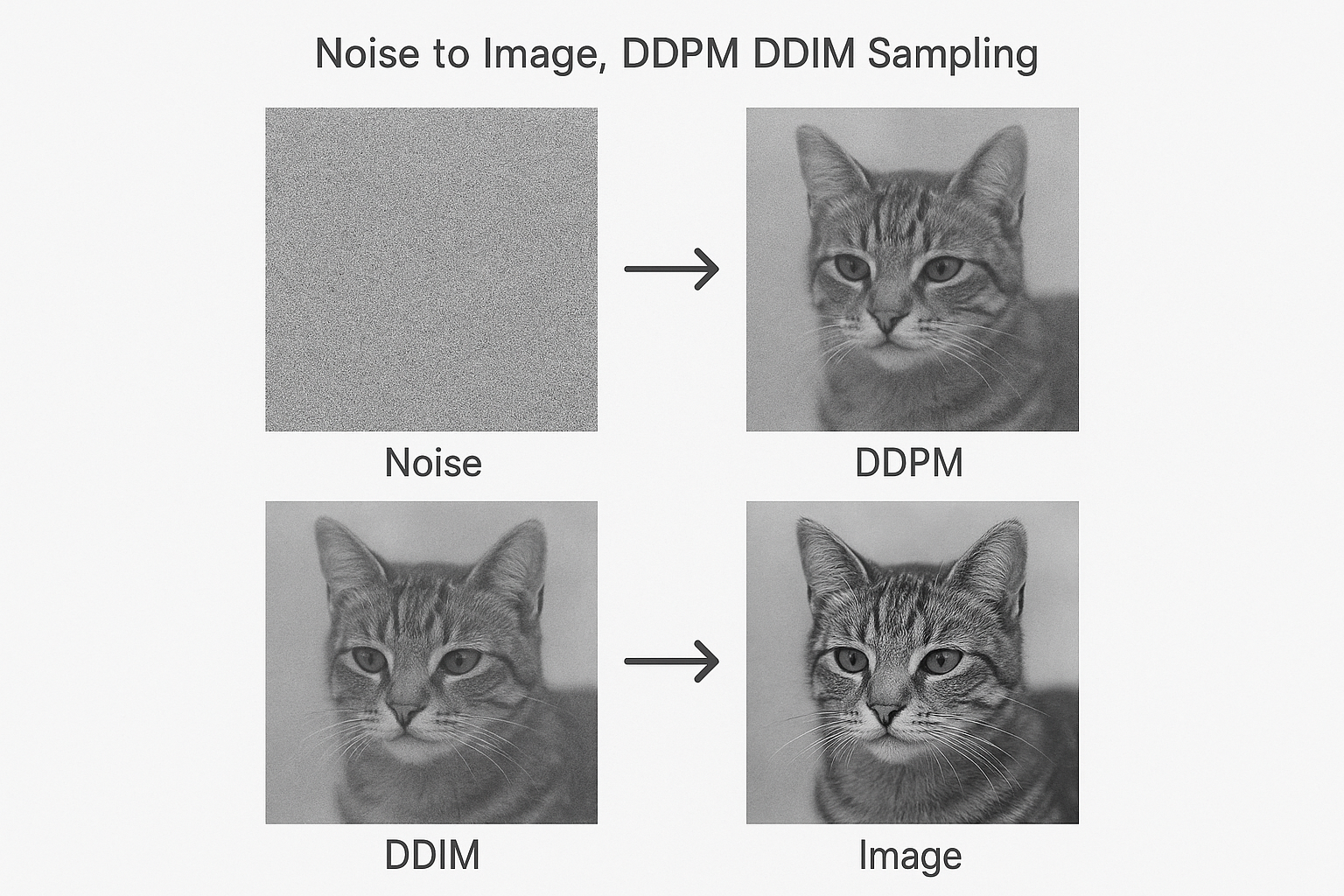
Model trained. Now generate images. Start with random noise, repeatedly denoise, arrive at a realistic image.
Part 6 of 7 in the Diffusion Models series.
DDPM sampling
Reverse the forward process step by step:
$$x_{t-1} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{\alpha_t}}\left(x_t - \frac{\beta_t}{\sqrt{1-\bar{\alpha}t}}\epsilon\theta(x_t, t)\right) + \sigma_t z$$
Where z ~ N(0, I) and σ_t is noise scale.
Interactive demo: Flow Matching Animation
DDPM sampler code
@torch.no_grad()
def ddpm_sample(model, shape, T=1000):
device = next(model.parameters()).device
# Start with pure noise
x = torch.randn(shape, device=device)
for t in reversed(range(T)):
t_batch = torch.full((shape[0],), t, device=device, dtype=torch.long)
# Predict noise
predicted_noise = model(x, t_batch)
# Compute coefficients
alpha = alphas[t]
alpha_bar = alpha_bars[t]
beta = betas[t]
# Mean
mean = (1 / torch.sqrt(alpha)) * (
x - (beta / torch.sqrt(1 - alpha_bar)) * predicted_noise
)
# Add noise (except at t=0)
if t > 0:
noise = torch.randn_like(x)
sigma = torch.sqrt(beta)
x = mean + sigma * noise
else:
x = mean
return x
Problem: 1000 steps is slow
Each step = full model forward pass. Generation takes minutes.
Solutions:
- DDIM: deterministic, fewer steps
- DPM-Solver: better ODE solver
- Distillation: train faster sampler
DDIM sampling
Deterministic sampling. Skip steps.
@torch.no_grad()
def ddim_sample(model, shape, steps=50, eta=0):
# Select timesteps to use
timesteps = torch.linspace(T-1, 0, steps, dtype=torch.long)
x = torch.randn(shape, device=device)
for i, t in enumerate(timesteps):
t_batch = torch.full((shape[0],), t, device=device)
predicted_noise = model(x, t_batch)
# DDIM update (simplified)
alpha_bar_t = alpha_bars[t]
alpha_bar_prev = alpha_bars[timesteps[i+1]] if i+1 < len(timesteps) else 1.0
# Predicted x_0
pred_x0 = (x - torch.sqrt(1 - alpha_bar_t) * predicted_noise) / torch.sqrt(alpha_bar_t)
# Direction pointing to x_t
dir_xt = torch.sqrt(1 - alpha_bar_prev - eta**2 * (1 - alpha_bar_prev) / (1 - alpha_bar_t) * (1 - alpha_bar_t / alpha_bar_prev)) * predicted_noise
# Random noise
noise = eta * torch.randn_like(x)
x = torch.sqrt(alpha_bar_prev) * pred_x0 + dir_xt + noise
return x
eta=0: deterministic eta=1: same as DDPM
50 steps instead of 1000. Similar quality.
Classifier-free guidance
Make outputs match condition more strongly:
$$\tilde{\epsilon}\theta = \epsilon\theta(x_t, \emptyset) + w \cdot (\epsilon_\theta(x_t, c) - \epsilon_\theta(x_t, \emptyset))$$
w > 1 amplifies conditioning. Typical: w=7.5
def guided_denoise(model, x, t, condition, w=7.5):
# Unconditional prediction
noise_uncond = model(x, t, condition=None)
# Conditional prediction
noise_cond = model(x, t, condition=condition)
# Guided combination
return noise_uncond + w * (noise_cond - noise_uncond)
Practical generation
# Generate 4 images
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
samples = ddim_sample(model, (4, 3, 256, 256), steps=50)
# Denormalize
samples = (samples + 1) / 2 # [-1, 1] → [0, 1]
samples = samples.clamp(0, 1)
# Save
save_image(samples, "generated.png", nrow=2)
Quality vs speed tradeoff
| Method | Steps | Quality | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| DDPM | 1000 | Best | Slow |
| DDIM | 50 | Good | Fast |
| DDIM | 20 | Okay | Very fast |
| DPM-Solver | 20 | Good | Fast |
Diffusion sampling techniques mastered! Give ML Animations a star and share this with fellow generative AI enthusiasts!