Before BERT: train models from scratch for each task. After BERT: pretrain once, fine-tune everywhere.
BERT showed that transformer encoders, pretrained on massive text, transfer amazingly to downstream tasks.
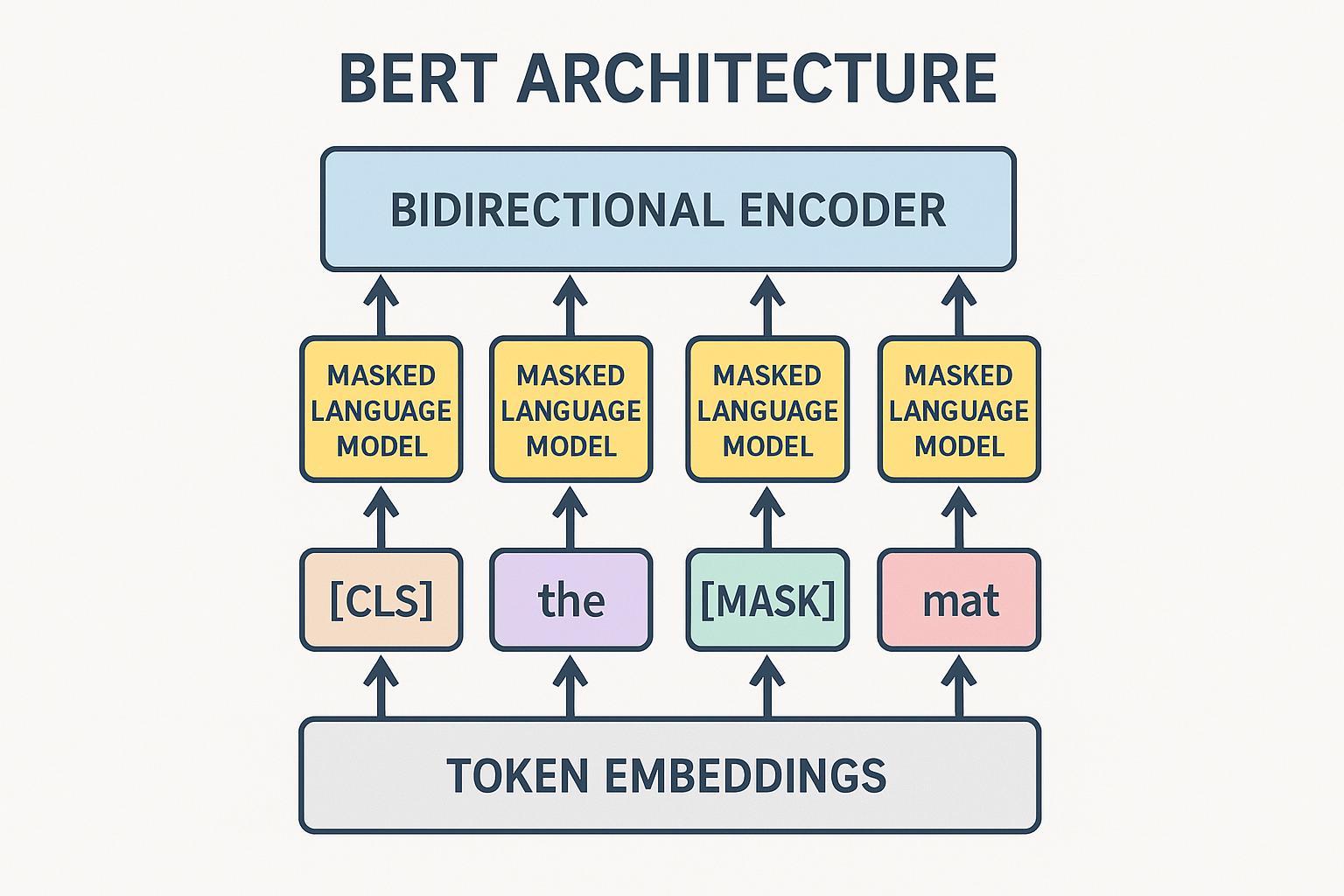
Key innovation: bidirectional
GPT: left-to-right only. Each position sees only previous tokens. BERT: bidirectional. Each position sees everything.
“The [MASK] sat on the mat”
BERT sees both “The” and “sat on the mat” to predict [MASK]. Much richer context.
Interactive demo: BERT Animation
Pretraining objectives
Masked Language Modeling (MLM)
- Take sentence
- Randomly mask 15% of tokens
- Predict the masked tokens
Not all masked tokens replaced with [MASK]:
- 80%: replace with [MASK]
- 10%: replace with random token
- 10%: keep original
This prevents model from only learning about [MASK] token.
Next Sentence Prediction (NSP)
Given two sentences, predict if B follows A.
50% real pairs, 50% random.
Later research showed this isn’t crucial. RoBERTa drops it.
Architecture
Encoder-only transformer.
BERT-base: 12 layers, 768 hidden, 12 heads, 110M params BERT-large: 24 layers, 1024 hidden, 16 heads, 340M params
Special tokens:
- [CLS]: classification token (first position)
- [SEP]: separator between sentences
- [MASK]: masked token placeholder
Using BERT
For classification
Use [CLS] token representation:
from transformers import BertModel
model = BertModel.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
outputs = model(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
cls_embedding = outputs.last_hidden_state[:, 0] # [CLS] position
# Add classifier head on top
For token tasks (NER, POS)
Use all token representations:
token_embeddings = outputs.last_hidden_state # (batch, seq, hidden)
# Add per-token classifier
For sentence pairs
[CLS] sentence1 [SEP] sentence2 [SEP]
Segment embeddings distinguish which sentence each token belongs to.
Fine-tuning
Key insight: pretrained representations are good starting point for almost any NLP task.
from transformers import BertForSequenceClassification
model = BertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
'bert-base-uncased',
num_labels=2
)
# Train on your task
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=2e-5)
for batch in dataloader:
outputs = model(**batch)
loss = outputs.loss
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
Small learning rate (2e-5). Few epochs (2-4). Don’t overfit.
Variants
RoBERTa: More data, longer training, no NSP, dynamic masking ALBERT: Parameter sharing, sentence order prediction DistilBERT: 40% smaller, 60% faster, 97% performance ELECTRA: Replaced token detection instead of MLM
Legacy
BERT dominated NLP for years. Showed:
- Pretraining + fine-tuning paradigm
- Transformers for understanding (not just generation)
- Importance of scale
Now GPT-style models dominate, but BERT patterns still relevant for efficient encoder models.
BERT understanding achieved! Show some love to ML Animations with a star and share with NLP enthusiasts!